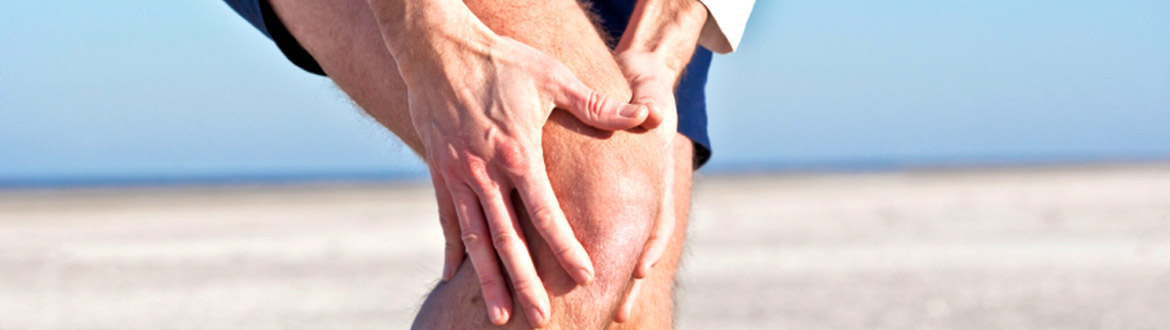
Arthroscopy is presently regarded as the reliable and commonly used diagnostic as well as a treatment procedure. In knee arthroscopy, the knee joint is viewed through a microscopic camera, known as the arthroscope. This facilitates a better vision of the knee joint. Thus, an accurate and reliable diagnosis can be achieved.
Statistics reveal that almost 4 million knee arthroscopy surgeries are performed in a year.
Before the surgery, a preoperative examination is conducted to check if the overall health status of the patient is well above satisfactory. This is also to ensure that there are no complications that can unnecessarily interfere with the surgery.
The surgery begins with the administration of anesthesia. Anesthesia is mostly local, that numbs only the particular part. This is followed by making small incisions on the knee. In certain cases, a small marking may be made to ensure that incisions are in the right place. As soon as the incisions are made, the knee joint is filled with sterile solution so as to wash away any fluids. This shall increase the vision. The use of high resolution monitors and cameras can further increase the quality of vision.
The arthoscope is injected and the detailed images are viewed in a monitor. If any treatment is essential, tiny instruments are inserted and the surgery is performed using instruments like scissors, lasers or motorized shavers etc. The whole procedure doesnt consume much time. Recovery is also much faster when compared to the conventional surgeries. However, the postoperative conditions like the presence of any swelling, weight bearing etc are looked for.
Knee arthroscopy is commonly done for the following situations:
- Torn anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction.
- Meniscus repair/removal.
- Removal of the loose cartilage or bone fragments.
- Trimming the torn articular cartilage pieces.
- Removal of inflamed synovial tissues.